Are you a property owner wondering if a septic system is suitable for your property with clay soil? Look no further! Our article will provide you with all the information you need to make an informed decision. Discover the pros and cons of using a septic system in clay soil, learn about potential challenges, and explore alternative options. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of whether a septic system is the right choice for your clay soil property. Let’s dig into the details and find out.
This image is property of www.ukdpsolutions.co.uk.
1. Understanding Clay Soil
1.1 What is clay soil?
Clay soil is a type of soil that is characterized by its fine particles and high water retention capacity. It has a unique texture and is often sticky and moldable when wet. Clay soil is composed primarily of minerals such as silica, alumina, and iron oxide, and it can be found in various colors, including shades of red, yellow, and brown.
1.2 Properties of clay soil
Clay soil has several distinct properties that differentiate it from other types of soil. One of the key features of clay soil is its high water-holding capacity, which can lead to poor drainage and prolonged water saturation. This can make the soil heavy and compact, leading to potential issues for septic systems. Additionally, clay soil has a tendency to shrink and expand with changes in moisture content, which can cause structural problems over time.
1.3 Challenges of clay soil for septic systems
Clay soil poses specific challenges for septic systems due to its poor drainage and potential for compaction. The high water-holding capacity of clay soil can result in slow percolation rates, making it difficult for septic systems to properly filter and treat wastewater. Additionally, the shrinkage and expansion properties of clay soil can lead to shifting and settling, which may compromise the integrity of septic system components. Therefore, it is essential to carefully assess the feasibility of installing a septic system on clay soil.
2. Assessing the Feasibility
2.1 Conducting a soil test
Before considering the installation of a septic system on clay soil, it is crucial to conduct a thorough soil test. A soil test will provide valuable information about the composition and characteristics of the soil, including its texture, drainage capabilities, and nutrient content. By obtaining this data, you can determine if clay soil is suitable for a septic system or if alternative options need to be explored.
2.2 Analyzing percolation rates
Percolation rates, also known as soil infiltration rates, measure how quickly water is absorbed by the soil. This is an essential factor to consider when evaluating the feasibility of a septic system on clay soil. A percolation test involves digging test holes and observing the rate at which water drains from them. If the percolation rates are low, it indicates that the soil may be too dense or impermeable for a septic system to function effectively.
2.3 Consulting with a professional
To ensure an accurate assessment of the feasibility of a septic system on clay soil, it is advisable to consult with a professional, such as a soil scientist or a septic system designer. These experts have the knowledge and experience to analyze soil test results and offer informed recommendations. They can provide valuable insights and guidance throughout the process to help you make an informed decision regarding the installation of a septic system.
This image is property of static.drainagesuperstore.co.uk.
3. Types of Septic Systems
3.1 Conventional septic system
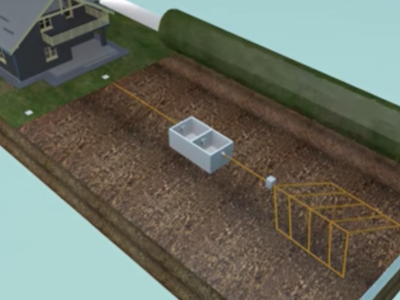
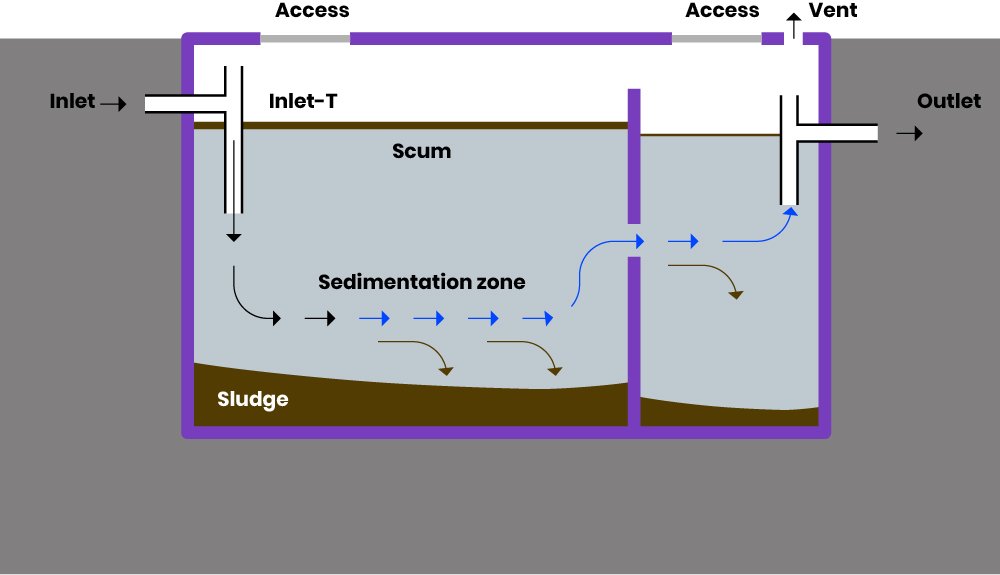
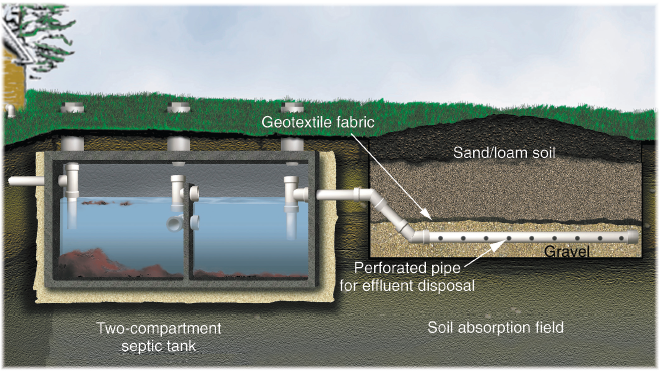
A conventional septic system consists of a septic tank and a drainfield. In this system, wastewater from the property is directed to the septic tank, where solid waste settles and is broken down by bacteria. The partially treated wastewater then flows into the drainfield, where it is further treated and absorbed into the surrounding soil. While conventional septic systems can work on clay soil, the slow percolation rates and poor drainage of clay soil may require additional considerations and modifications.
3.2 Aerobic septic system
An aerobic septic system is an alternative to the conventional system and utilizes an aerobic treatment process. This system introduces oxygen into the wastewater to enhance the breakdown of organic matter by aerobic bacteria. Aerobic septic systems can be more effective in treating wastewater in clay soil as the increased aeration can improve the breakdown of organic matter and help mitigate the slow percolation rates.
3.3 Alternative systems for clay soil
In some cases, clay soil may require alternative septic system options. These may include specialized systems designed specifically for challenging soil conditions. Examples of alternative systems for clay soil include pressure distribution systems, mound systems, and sand filter systems. These systems are designed to work effectively in soils with slow percolation rates, ensuring proper treatment and disposal of wastewater.
4. Proper Site Selection
4.1 Determining suitable location
When installing a septic system on clay soil, choosing the right location is crucial. The site should be selected based on factors such as soil composition, topography, and distance from water sources. The chosen location should have well-drained areas of clay soil that can adequately accommodate the septic system components and allow for proper wastewater treatment and dispersal.
4.2 Considering setbacks and regulations
Local regulations and setback requirements play a significant role in determining the appropriate site for a septic system. Setbacks are the minimum distances that must be maintained between septic system components and features such as wells, property lines, and bodies of water. It is important to familiarize yourself with these regulations and ensure compliance when selecting a site for a septic system on clay soil.
4.3 Factors to prioritize
When evaluating potential sites, several factors should be prioritized. These factors include percolation rates, soil depth, slope, and proximity to groundwater sources. Percolation rates should be within acceptable limits to ensure proper wastewater treatment and minimize the risk of contamination. Additionally, the soil should be deep enough to provide sufficient treatment capacity, and the site should have a slope that promotes adequate drainage.
This image is property of agrilife.org.
5. Preparing the Clay Soil
5.1 Soil conditioning techniques
Preparing clay soil for a septic system involves utilizing soil conditioning techniques to improve its drainage characteristics. One commonly used technique is deep ripping, which involves mechanically breaking up the compacted soil layers to increase pore space and enhance water movement. Other techniques may include subsoiling, which helps alleviate compaction, and soil aeration, which improves oxygen exchange in the soil.
5.2 Adding organic matter
The addition of organic matter can significantly improve the structure and drainage capabilities of clay soil. Materials such as compost, aged manure, and peat moss can be incorporated into the soil, increasing its ability to retain nutrients and moisture while promoting better drainage. Adding organic matter also enhances the soil’s overall fertility and promotes the growth of beneficial soil organisms.
5.3 Improving drainage
Improving the drainage of clay soil is vital for the efficient functioning of a septic system. Installing drainage systems, such as French drains or perforated pipes, can help redirect excess water away from the septic system area. Additionally, creating gentle slopes or grading the land can prevent water from pooling and ensure adequate drainage. Proper grading should be considered during the site preparation process.
6. Size and Design Considerations
6.1 Determining appropriate size
The size of a septic system is determined based on the anticipated daily wastewater flow from the property. When installing a septic system on clay soil, it is essential to consider the percolation rates and the potential limitations of clay soil in treating and dispersing wastewater. Therefore, it may be necessary to design a larger system to ensure adequate treatment and prevent overloading of the soil.
6.2 Importance of compartmentalization
Compartmentalization is an important aspect of septic system design, especially when dealing with clay soil. By incorporating multiple compartments within the septic tank, solids can be more effectively settled and separated from the wastewater. This helps prevent clogging and reduces the potential for damage to drainfield pipes due to the passage of solid particles.
6.3 Accounting for future growth
When designing a septic system for clay soil, it is essential to consider potential future growth and increased wastewater flow. Allowing for additional capacity in the design can prevent the need for system modifications or replacements in the future. By accounting for future growth, you can ensure that the septic system will continue to meet the needs of the property for years to come.

This image is property of static.drainagesuperstore.co.uk.
7. Percolation Solutions
7.1 Addressing slow percolation
Slow percolation rates in clay soil can be problematic for septic systems. To address this issue, a variety of solutions can be implemented. One option is to install pretreatment devices, such as media filters or aerobic treatment units, which can enhance the treatment of wastewater before it reaches the drainfield. Additionally, periodic maintenance, such as desludging the septic tank, can help prevent the buildup of solids and improve percolation rates.
7.2 Installing a drainfield
The drainfield is a critical component of a septic system that disperses treated wastewater into the soil. When dealing with clay soil, the drainfield design must accommodate the slow percolation rates. This can be achieved by increasing the size of the drainfield or utilizing specialized drainfield materials, such as gravel or sand, that provide better drainage capabilities.
7.3 Utilizing alternative drainfield options
In some cases, alternative drainfield options may be necessary for clay soil. These options can include above-ground sand mounds, pressure distribution systems, or gravel-less chambers. These alternative drainfield designs provide improved treatment and dispersal of wastewater in soils with slow percolation rates. However, it is crucial to consult with a professional to determine the most suitable alternative option based on the specific characteristics of the clay soil.
8. Maintenance and Care
8.1 Creating a regular maintenance schedule
Maintaining a septic system installed on clay soil requires adherence to a regular maintenance schedule. This includes routine inspections of the system, periodic pumping of the septic tank, and monitoring of the drainfield performance. By following a maintenance schedule, you can identify and address issues before they escalate, ensuring the long-term functionality of the septic system.
8.2 Monitoring water usage
Clay soil is particularly susceptible to becoming waterlogged, especially during periods of heavy rainfall. It is important to monitor water usage within the property to prevent overloading the septic system and potentially saturating the clay soil. Implementing water conservation measures, such as fixing leaks, using water-efficient appliances, and spreading out water usage, can help minimize the strain on the septic system and the soil.
8.3 Avoiding septic system overloading
To prevent overloading the septic system and compromising the effectiveness of the soil treatment, it is crucial to avoid excessive water usage and the disposal of non-biodegradable or harmful substances down the drains. These substances can clog the system or inhibit the natural breakdown of organic matter. Proper waste management practices should be followed, including the regular pumping of the septic tank and the appropriate disposal of household chemicals and medications.

This image is property of i0.wp.com.
9. Common Issues and Troubleshooting
9.1 Signs of septic system problems
Being aware of the signs of septic system problems is essential for early detection and prompt resolution. Common signs of septic system issues include foul odors, slow draining fixtures, gurgling sounds from plumbing fixtures, sewage backups, and unusually lush or wet areas near the drainfield. If any of these signs are observed, it is important to address them promptly to prevent further damage and potential health hazards.
9.2 Addressing clay-related issues
Clay-related issues, such as poor drainage, soil compaction, and shifting, can impact the functionality of a septic system. These issues can be addressed by implementing proper soil conditioning techniques, adding organic matter, and improving drainage. Regular maintenance and monitoring can also help identify and rectify any clay-related issues before they escalate.
9.3 Seeking professional assistance
If you are experiencing persistent problems with your septic system on clay soil, seeking professional assistance is recommended. A qualified septic system professional can conduct a thorough assessment of the system, diagnose any issues, and provide appropriate solutions. Their expertise can help ensure the optimal functioning and longevity of the septic system on clay soil.
10. Other Considerations
10.1 Impact of landscaping choices
The choice of landscaping around a septic system can have an impact on its functionality and the performance of the clay soil. It is important to select plants that have shallow root systems and are tolerant of the soil conditions. Avoiding dense vegetation or trees with invasive root systems can prevent damage to septic system components and help maintain the integrity of the clay soil.
10.2 Effect of weather conditions
Weather conditions, such as heavy rainfall or drought, can significantly affect the performance of a septic system on clay soil. Excessive rainfall can saturate the clay soil and hinder percolation rates, while extended periods of drought can lead to soil shrinkage and cracking. It is important to be mindful of these weather conditions and implement appropriate measures, such as water conservation practices during droughts or stormwater management strategies during heavy rainfall.
10.3 Potential need for periodic soil tests
Periodic soil tests may be necessary to assess the long-term viability of a septic system on clay soil. Over time, soil conditions can change, and issues such as compaction or clogging can develop. Conducting soil tests at regular intervals can help identify any changes in the soil properties and guide appropriate maintenance or corrective actions. Regular soil testing can ensure the ongoing functionality and effectiveness of the septic system.

